THE ALGA PADINA PAVONICA AS A POSSIBLE ANTIBACTERIAL AGENT IN BIOMATERIALS
Bioactive glasses are innovative biocompatible materials that are widely used in the clinical field of regeneration and repair of bone tissue defects. Therefore, the possibility of creating biomaterials with antibacterial properties is of particular importance, given the detrimental role of bacterial infections in tissue healing processes. In this context, bioactive glasses were realized with an extract of P. pavonica alga and / or with silver nanoparticles (with known antimicrobial activity), on which the growth of the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus was evaluated. The results obtained showed the marked ability of the algal extract, rich in polyphenols, in enhancing the antibacterial activity of the silver nanoparticles. This study further confirms that the biodiversity of marine organisms constitutes an almost inexhaustible and still unexplored reserve of biologically active secondary metabolites.
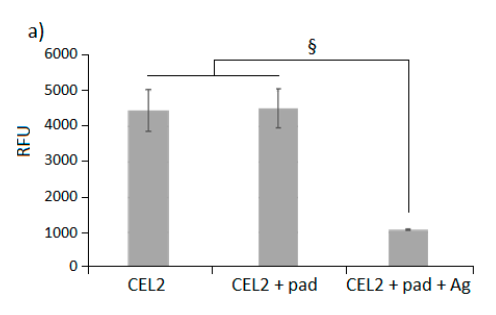
In figure: Staphylococcus aureus growth (y-axis, Relative Fluorescence Unit) on bioactive glass CEL2, CEL2 functionalized with P. pavonica and CEL2 functionalized with the alga and silver nanoparticles.
REFERENCE TO A WEBSITE OR TO A LINK
Sayed Abdelgeliel, A., Ferraris, S., Cochis, A., Vitalini, S., Iriti, M., Mohammed, H., Kumar, A., Cazzola, M., Salem, W.M., Verné, E. and Spriano, S., 2019. Surface Functionalization of Bioactive Glasses with Polyphenols from Padina pavonica Algae and In Situ Reduction of Silver Ions: Physico-Chemical Characterization and Biological Response. Coatings, 9(6), p.394. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9060394.